Diamond Information
Diamonds and precious stones have been used as symbols of status, wealth and power for millennia. They have also been used as a hedge against inflation and a means of transporting great wealth. Ownership of them has also obviated the need to balance the relative risks of different currencies.
Diamonds form approximately 90% of the global gem market in terms of value and are currently traded worldwide in US Dollars. The market price of a white diamond is relatively well defined according to grading in terms of the 4 C’s - Cut, Clarity, Colour and Carat.
Integral to this process is the accurate grading of and certification of stones. Although there are many grading certificates available, the certificates viewed most favourably by the trade are those issued by the GIA (Gemmological Institute of America), AGS (American Gemmological Society) for ideal cut diamonds and the HRD (High Council of Diamonds in Antwerp). Most high value diamonds will have one of these certificates.
Topset Jewellery only deal in conflict-free diamonds and all of our transactions are covered by the Kimberley Process (KP); a joint government, industry and civil society initiative to stem the flow of conflict diamonds being sold around the world.
4 C's of Diamonds
Cut
Clarity
Colour
Carat
Cut
There are two meanings associated with cut for diamonds.
Firstly, the cut refers to the shape and faceting of the diamond. Round brilliant cut is the most popular used in diamond jewellery around the world. All other shapes are known as fancy shapes, examples of these include the cushion, oval, princess, asscher, radiant, emerald and marquise.
Secondly, the cut refers to the symmetry of the stone's facets, its overall proportions, and its ability to reflect light. An expertly-cut diamond will achieve high levels of brilliance, sparkle, and fire. Even if a diamond is graded well in other areas, a poor cut can result in a dull, muted effect. The brilliance of a diamond the total light reflected from a diamond. The sparkle of the diamond refers to the pattern of light and dark areas and the flashes of light, or sparkle, when a diamond is moved. The fire of the diamond the dispersion of light into the colours of the spectrum.
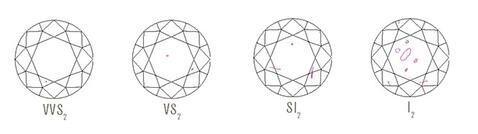
Clarity
Diamond clarity refers to the absence of inclusions and blemishes. In determining a clarity grade, the size, nature, position, colour or relief are considered, along with the quantity of clarity characteristics visible under 10× magnification.
Flawless (FL) - No inclusions or blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10× magnification
Internally Flawless (IF) - No inclusions and only blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10× magnification
Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1and VVS2) - Inclusions are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10× magnification
Very Slightly Included (VS1and VS2) - Inclusions are minor and range from difficult to somewhat easy for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification
Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2) - Inclusions are noticeable to a skilled grader under 10x magnification
Included (I1, I2, and I3)- Inclusions are obvious under 10× magnification and may affect transparency and brilliance
Colour
Diamonds are valued by how closely they approach colourlessness – the less colour, the higher their value. Most diamonds found in jewellery stores run from colourless to near-colourless, with slight hints of yellow or brown. GIA’s colour-grading scale for diamonds is the industry standard. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colourless, and continues with increasing presence of colour to the letter Z, or light yellow or brown. Each letter grade has a clearly defined range of colour appearance. Diamonds are colour-graded by comparing them to stones of known colour under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions.
Carat
The carat, the standard unit of weight for diamonds and other gemstones, takes its name from the carob seed. Because these small seeds had a fairly uniform weight, early gem traders used them as counterweights in their balance scales. The modern metric carat is equal to 0.2 grams. Diamonds and other gemstones are weighed in metric carats, with a carat being divided into 100 points.
Please click on the link below to view a chart of the different diamond sizes:
Coloured Diamonds
Coloured diamonds, are the rarest of diamonds and renowned for their beauty, encompassing a wonderful palate of colour including pinks, champagnes, cognacs, yellows, greens, blues, oranges and even reds.
Particular care has to be taken to avoid treated stones (usually irradiation) and certification is necessary to make sure you are buying a natural coloured diamond. Because the price per carat of natural coloured diamonds is so high one should have GIA certification of stones over 0.20ct.